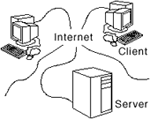
(or WWW, or Web)
- is all of the information available on the Internet.
This information is made available by computers running software
to give it out (Web servers) according to a set of
rules (http, ftp, etc.) that are understood by
browsers (like Netscape and Internet
Explorer) -- other pieces of software running on
other computers around the world.
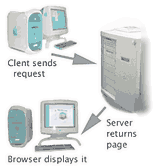
So, when we start surfing the Web, we
(1) sit down at a
client computer running a browser,
which
(2) "calls up"
another computer, the server running the Web server
software, to ask for the information that we want, and
(3) the server
sends it across the Internet to the browser, which
then
(4) displays it
for us to see.
- Interactions on the Web consist of a client
computer requesting a document from a server,
and
- the software on the client is a browser that
displays the information obtained, while the server runs
Web server software that answers requests
coming from browsers.
- The transaction to display a page consists of
the client requesting the page, server delivering it,
and browser (client) displaying it. Sort
of -- this actually happens for each
text page and image separately: this page required
four requests and deliveries for you to view it
in your browser...
|
|
Gavin's HHMI 02 Web Workshop: Web Info 1
Last Modified: Thu May 30 12:50:25 EDT 2002
Comments to
glarose@umich.edu
©2002 Gavin LaRose, UM Math
Dept
 The World Wide Web
The World Wide Web
 The World Wide Web
The World Wide Web
